Can we estimate results of In Vitro Fertilization? What are the chances of a successful embryo transfer? What do embryo quality and grading mean? Do they tell anything about possible outcomes? These are the questions intended parents worry about the most. While embryo grading is a complex medical process, parents need and should be informed about every important step on their fertility journey.
What do Embryo Quality and Grading Mean?
Embryologists use embryo grading system in order to make predictions about embryo transfer results. These predictions do not depict the reality accurately. A lot of embryos with low or middle grading lead to successful pregnancies. Moreover, not all high quality graded embryos result in gestation. This happens mainly because grading does not give an information about embryo’s genetics.
Embryo grading system is still a powerful tool that gives a good impression about which embryos are appropriate for transferring / freezing. Estimating embryo’s quality and potential is an important step. It helps intended parents to save time, finances, protects from unexpected misfortune and may facilitate their parenthood journey.
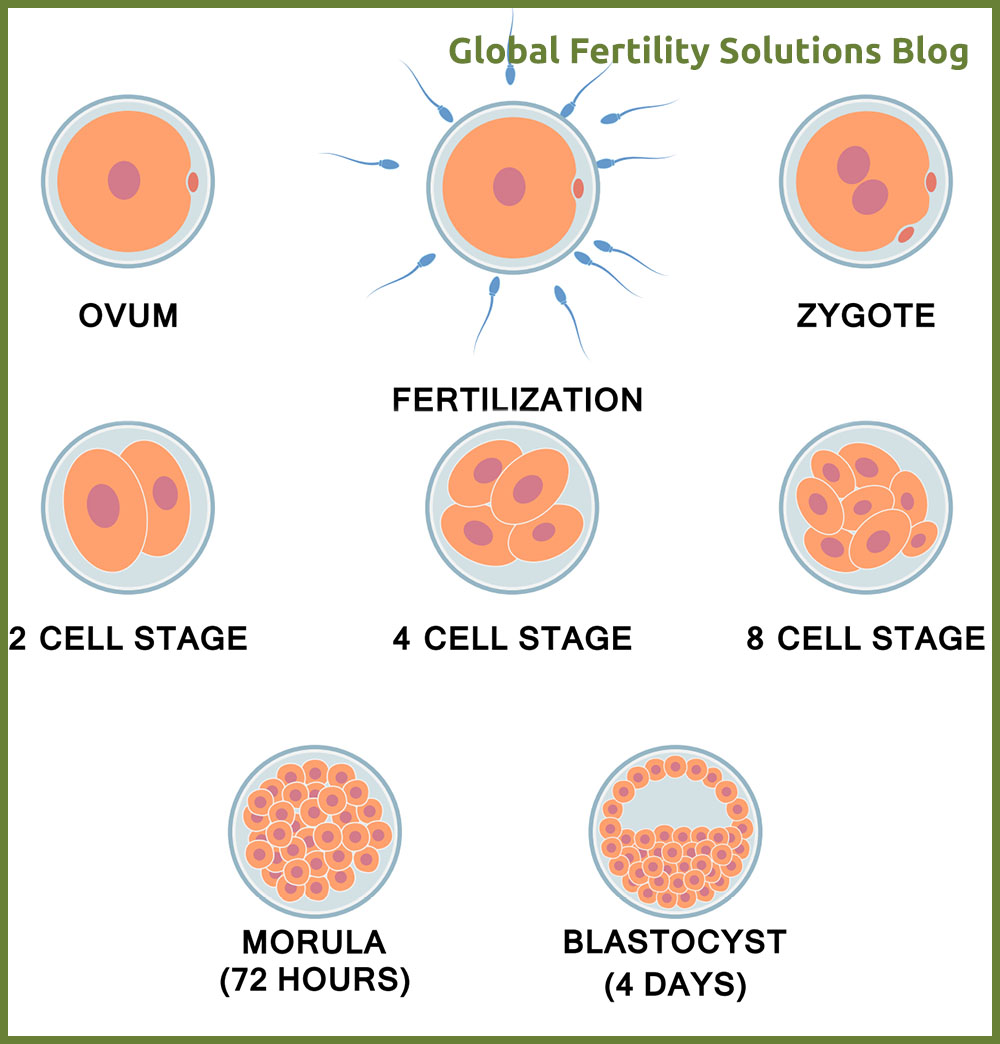
There is no universal grading system. In some clinics grade 1 is better than 4, while in others 4 may indicate the best quality. The most common practice is to observe an embryo after 3 or 5 days of fertilization. However, embryos are not on the same development stage on these days. Embryologists use different grading systems for day 3 and day 5.
Grading on day 3
On the day 3, embryos are on their “cleavage stage”. This means that cells in the embryo (blastomeres) are dividing. Observation happens under a high power microscope. On the day 3 after retrieval, embryo itself is not growing in size – only the cells are being replicated.
Accordingly, grading criteria number one is the number of cells in the embryo. The desired number of cells on the day 3 is 6-10. Based on experience, embryos containing 6 to 10 blastomeres on day 3, are more likely to result in successful pregnancy.
Criteria number 2 is the presence of fragmentation. Fragmentation/Blebbing is the process when the inside of the cells break off and form fragments. These blebs do not contain nucleus. Nucleus is the cell storing cell’s genetic material, DNA. As fragments/blebs are separated from the nucleated part of the cell, they are not referred to as cells. It is preferable to have little or no fragmentation at all. On the other hand, embryologists may capture multinucleation (presence of more than one nucleus per cell). Multinucleation is very hard to identify but may unfortunately indicate chromosomal abnormality of the embryo.
Embryo quality and grading includes one more important criteria – cell regularity. It is desired that blastomeres are of the same or close to the same size.
After the observation on the day 3, embryos having no fragmentations and including equally sized 6-10 cells will be considered of high quality and will be assigned the highest grade. Laboratory will assign further grades according to their own system. The higher the quality grades are, so is the likelihood of successful implantation.
Grading on day 5
On the 5th day after fertilization,embryo contains increased number of cells and a fluid cavity. As the cells are growing, they start to form in different types. We encounter two cell types on the day 5. First type forms the Inner Cell Mass (ICM) and the second one is called Trophectoderm Epithelium (TE). Day 5 embryo is referred to as Blastocyst and has reached the development stage when it is getting ready to attach itself to the uterine lining (Implantation).
ICM will grow into fetus and TE will form pregnancy essential tissues. Due to their importance for gestation, day 5 grading system evaluates both cell types separately. ICM and TE will be both observed for their amount and density (how tightly are they packed). For example a lot of tightly packed cells indicate higher quality than loosely packed fewer ones.
Blastocyst should implant soon. Above mentioned cell types divide and fluid cavity has to enlarge and hatch out of its shell. Fluid cavity’s volume in the embryo is one more criteria of 5th day grading. It should begin to outgrow the space inside of the shell (zona pellucida) and then the blastocyst will be ready for the implantation.
Day 5 embryo will be assigned the higher quality grade, when fluid cavity has reached the appropriate volume, ICM is tightly packed, is sufficient in amount and TE is also forming a cohesive layer with sufficient quantity of cells.
As already mentioned, clinics may use different grading systems and utilize numbers or symbols to assign grades. However, most of the laboratories use exactly above mentioned criterias to evaluate the potential of an embryo.
While talking about the chances of successful gestation, high embryo quality and grading is not a 100% guarantee. There are far more details included in the successful outcome. Sometimes an embryo does not implant because it has a genetic or chromosomal abnormality. It also happens that a lower grade embryo results in an unproblematic gestation because it has healthy genetics. A lot of clinics will suggest doing preimplantation genetic screening(PGS). This procedure checks chromosomal normality in the embryo.
Positive results in PGS and middle to high graded embryo already give a reasonable purpose to estimate a healthy pregnancy.
